编码一定是程序员永远的痛,不知道老高能不能救到你。
以下命令的操作环境:centos6 + python2.6
基础知识
Unicode
Unicode用数字0-0x10FFFF来映射字符,最多可以容纳1114112个字符,或者说有1114112个码位,理论上是足够用的。
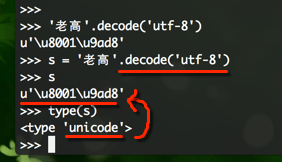
在python中如何找到Unicode?
UTF-8
UTF-8(8-bit Unicode Transformation Format)指的是Unicode的一种压缩方式,UTF-8用1到6个字节编码UNICODE字符,长度不定。
Unicode符号范围 | UTF-8编码方式
(十六进制) | (二进制)
--------------------+---------------------------------------------
0000 0000-0000 007F | 0xxxxxxx
0000 0080-0000 07FF | 110xxxxx 10xxxxxx
0000 0800-0000 FFFF | 1110xxxx 10xxxxxx 10xxxxxx
0001 0000-0010 FFFF | 11110xxx 10xxxxxx 10xxxxxx 10xxxxxx
老 高的Unicode编码是C0CF B8DF,UTF-8的编码是 \xe8\x80\x81 \xe9\xab\x98,\x表示后面两位数字是16进制,的我们把\x去掉,得到e88081 e9ab98,将其转为二进制,得到:
11101000 10000000 10000001
11101001 10101011 10011000
1110xxxx 10xxxxxx 10xxxxxx <----- 落到了上表的第三个区间
ASCII兼容
GBK汉字内码扩展规范,简称国标。 GB2312信息交换用汉字编码字符集。 大五码(Big5),又称为大五码或者五大码,是通行于台湾、香港地区的一个繁体字编码方案。
你能说出划线部分都是什么编码格式吗?
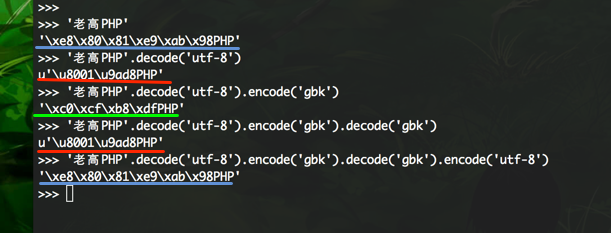
顺便扒一扒最近很火的能让IOS死机的字符
编码检测工具
pip install chardet
### 使用方法
from chardet import detect
print detect('abc')
get:
{'confidence': 1.0, 'encoding': 'ascii'}
编码实验
实验1
s = '老高@phper'
detect(s)
get:
{'confidence': 0.75249999999999995, 'encoding': 'utf-8'}
猜测1:python高版本中字符初始化直接为unicode编码。
实验2
s = '老高@phper'
u = s.decode('utf-8')
u
u.encode('gbk')
s.encode('gbk')
get:
>>> u
u'\u8001\u9ad8@phper'
>>> u.encode('gbk')
'\xc0\xcf\xb8\xdf@phper'
>>> s.encode('gbk')
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
UnicodeDecodeError: 'ascii' codec can't decode byte 0xe8 in position 0: ordinal not in range(128)
猜测2:字符编码的转换必须经过unicode,即如果需要将utf-8转为gbk,必须decode后encode。
你知道decode和encode都是做什么的吗?
实验3
# 接上面
type(s)
type(u)
a = dir(s)
b = dir(u)
list(set(a) ^ set(b))
get:
>>> type(s)
<type 'str'>
>>> type(u)
<type 'unicode'>
>>> a = dir(s)
>>> b = dir(u)
>>> list(set(a) ^ set(b))
['isdecimal', 'isnumeric']
>>>
猜测3:普通的str与unicode没有什么区别,[‘isdecimal’, ‘isnumeric’]两个方法是unicode类独有的。
reference:
https://docs.python.org/2/library/stdtypes.html?highlight=isdecimal#unicode.isnumeric